IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements;
According to IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements, a complete set of financial statements has the following components: Other reports and statements in the annual report (such as a financial review, an environmental report or a social report) are outside the scope of IAS 1.
- a statement of financial position
- a statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income (or statement of profit or loss with a separate statement of other comprehensive income)
- a statement of changes in equity
- a statement of cash flows (discussed in a later chapter)
- accounting policies note and other explanatory notes
- a statement of financial position at the beginning of the earliest comparative period when an entity applies an accounting policy retrospectively or corrects an error retrospectively.

Other reports and statements in the annual report (such as a financial review, an environmental report or a social report) are outside the scope of IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements.
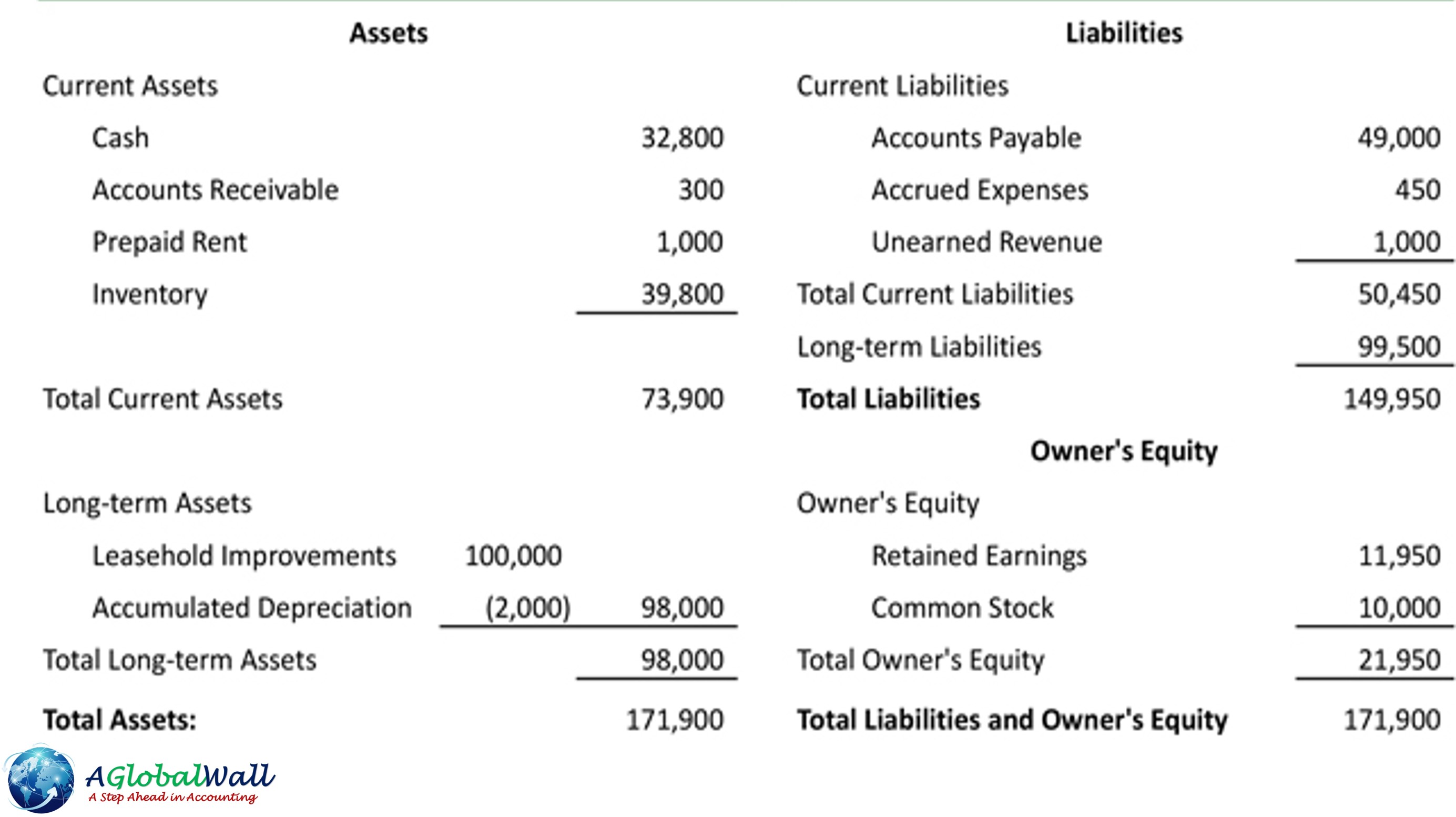
Statement of Financial Position
IAS 1 says that an entity must classify an asset as current on the statement of financial position if:
- it is realized or consumed during the entity’s normal trading cycle, or
- it is held for trading, or
- it will be realized within 12 months of the reporting date.
All other assets are classified as non-current.
IAS 1 says that an entity must classify a liability as current on the statement of financial position if:
- it is settled during the entity’s normal trading cycle, or
- it is held for trading, or
- it will be settled within 12 months of the reporting date.
All other liabilities are classified as non-current.
Statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income
IAS 1 provides the following definitions: Other comprehensive income (OCI) are incomes and expenses recognized outside of profit or loss, as required by particular IFRS Standards. Total comprehensive income (TCI) is the total of the entity’s profit or loss and other comprehensive income for the period. IAS 1 requires that OCI is classified into two groups as follows:
- items that might be reclassified (or recycled) to profit or loss in subsequent accounting periods:
– foreign exchange gains and losses arising on translation of a foreign operation (IAS 21)
– effective parts of cash flow hedging arrangements (IFRS 9)
– Remeasurement of investments in debt instruments that are classified as fair value through OCI (IFRS 9)
- items that will not be reclassified (or recycled) to profit or loss in subsequent accounting periods: – changes in revaluation surplus (IAS 16 & IAS 38)
– remeasurement components of defined benefit plans (IAS 19)
– remeasurement of investments in equity instruments that are classified as fair value through OCI (IFRS 9)
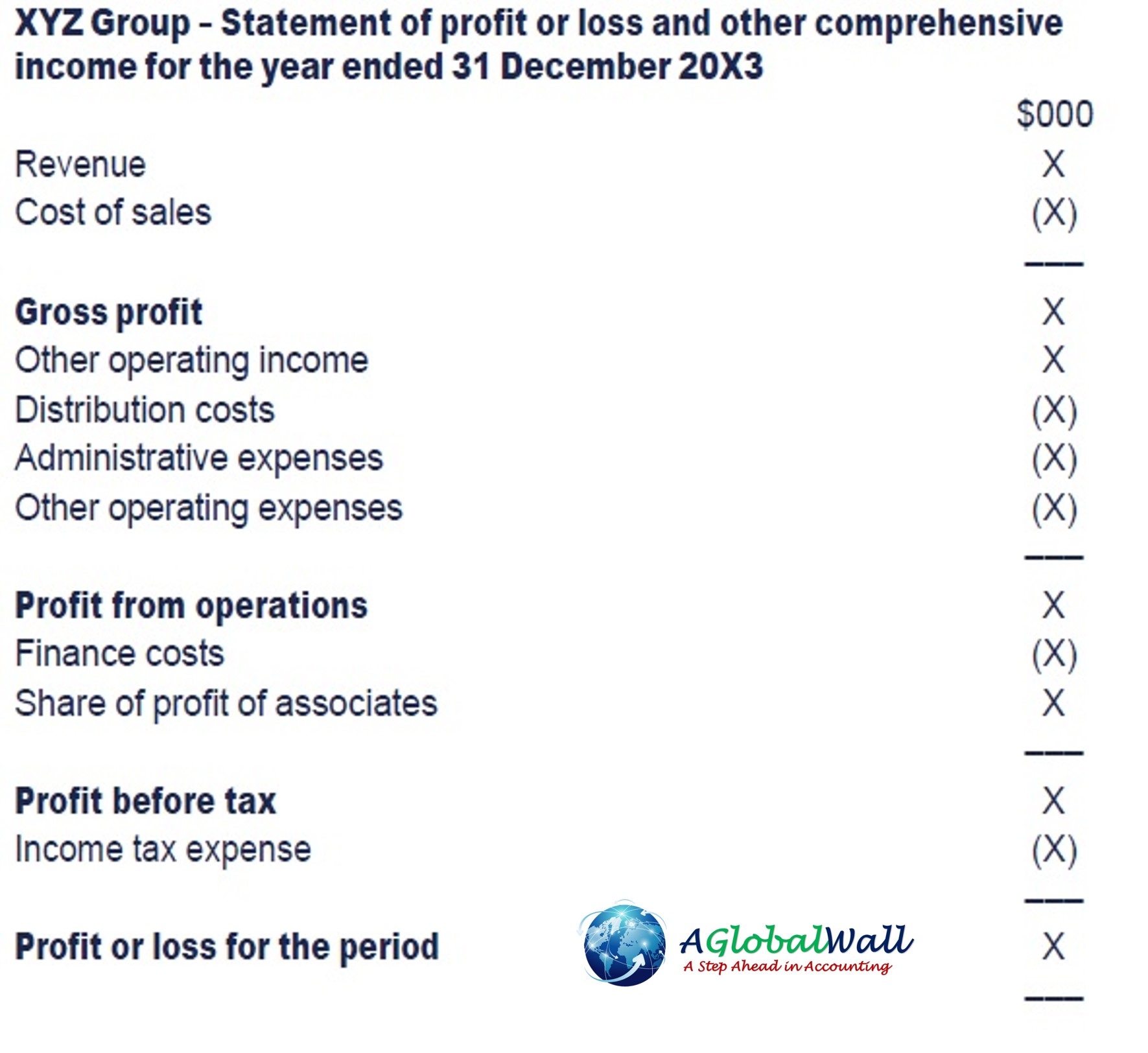
Entities can prepare one combined statement showing profit or loss for the year and OCI. Alternatively, an entity can prepare a statement of profit or loss and a separate statement of OCI. If the latter option is chosen, the statement of OCI should begin with profit or loss for the year so that there is no duplication or confusion as to which items are included within each statement.
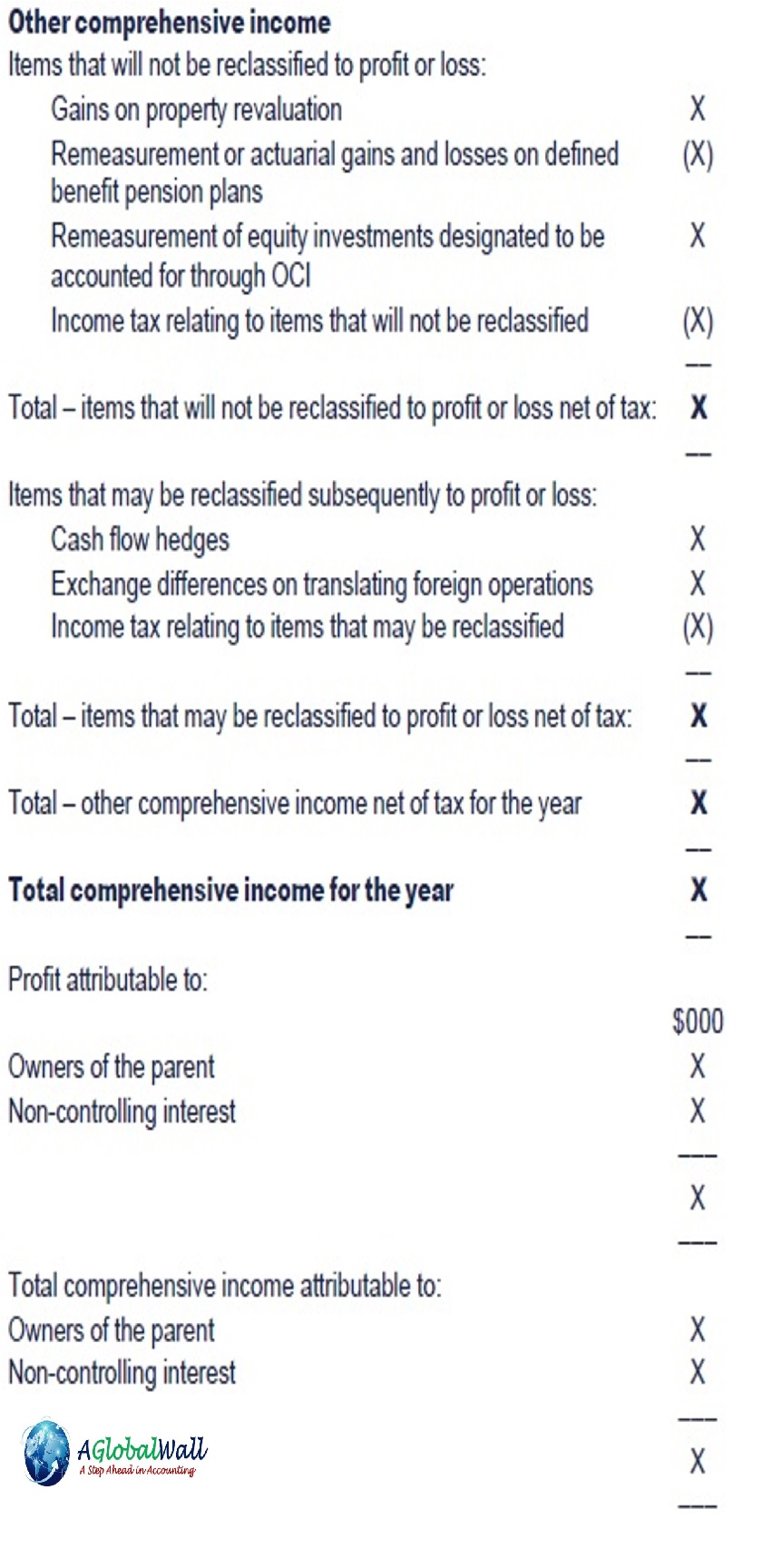
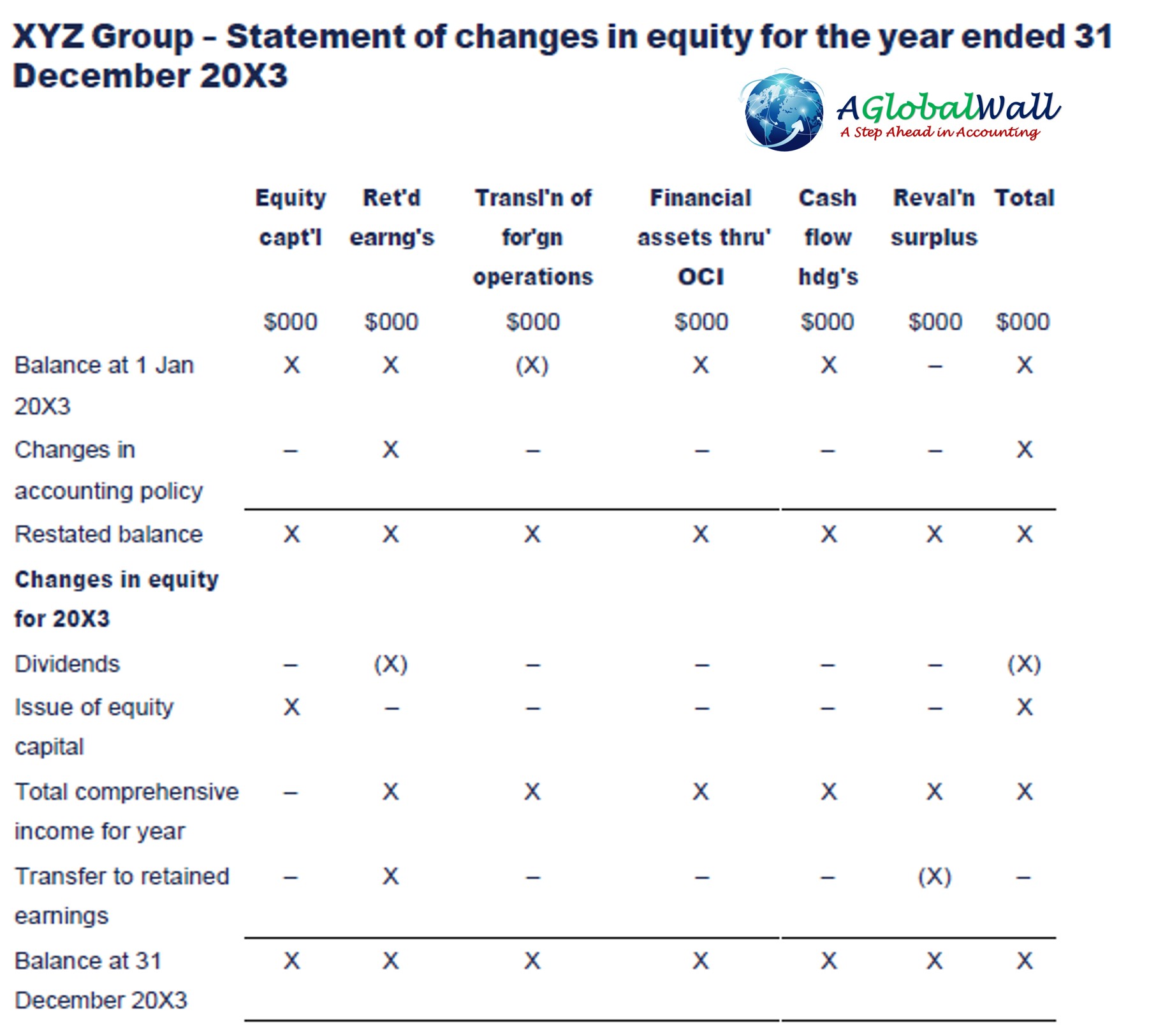
Statement of changes in equity
IAS 1 requires all changes in equity arising from transactions with owners in their capacity as owners to be presented separately from non-owner changes in equity. This would include:
- Issues of shares
- Dividends.
Total comprehensive income is shown in aggregate only for the purposes of reconciling opening to closing equity.
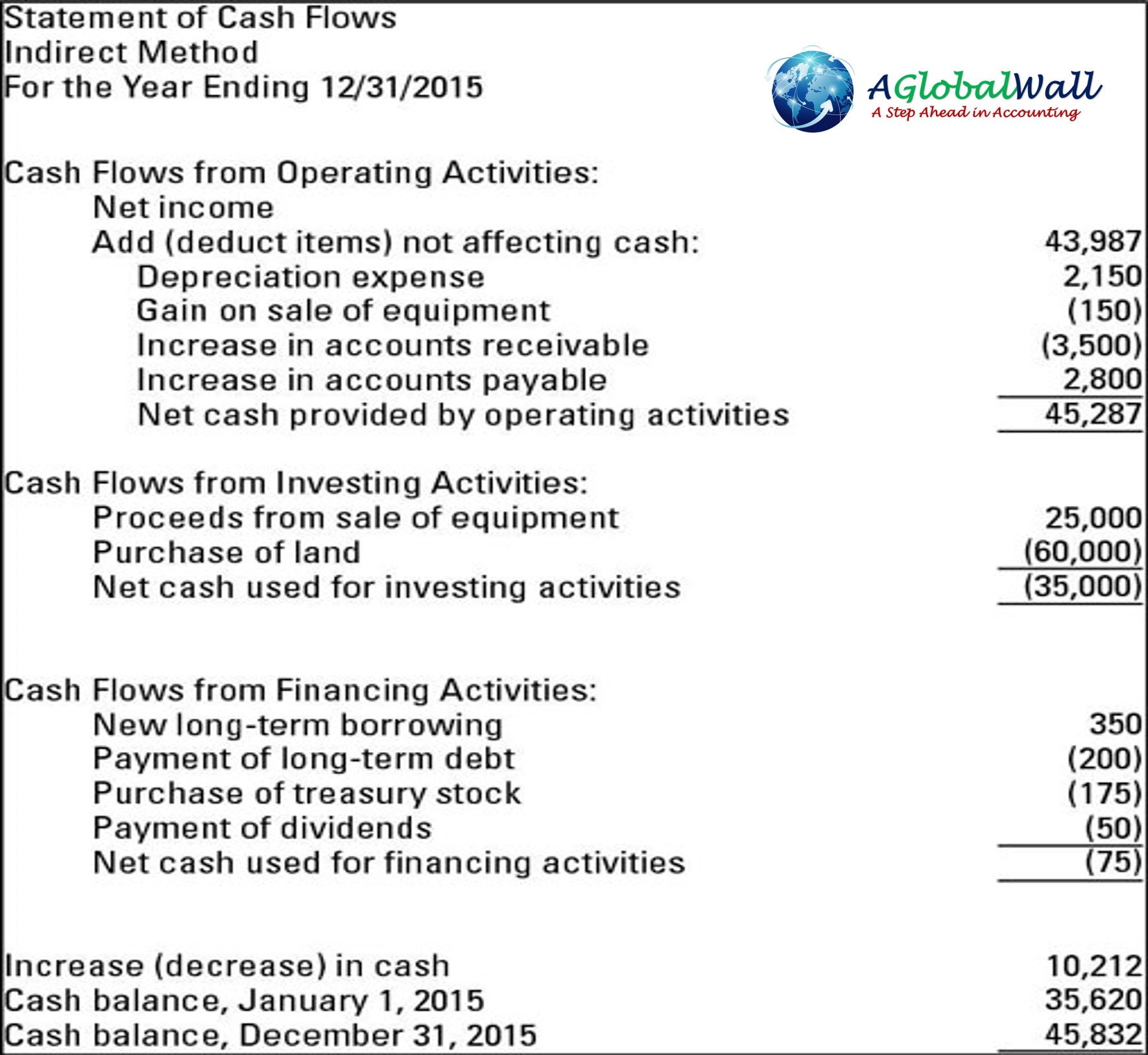
Statement of Cash Flows
General features of financial statements
Going concern Once management has assessed that there are no material uncertainties as to the ability of an entity to continue for the foreseeable future, the financial statements should be prepared on the assumption that the entity will in fact continue. In other words, the financial statements will be prepared on a going concern basis.
Accruals basis of accounting The accruals basis of accounting means that transactions and events are recognized when they occur, not when cash is received or paid for them.
The consistency of presentation The presentation and classification of items in the financial statements should be retained from one period to the next unless:
- it is clear that a change will result in a more appropriate presentation, or • a change is required by an IFRS or IAS Standard.
Materiality and aggregation An item is material if its omission or misstatement could influence the economic decisions of users taken on the basis of the financial statements. This could be based on the size or nature of an omission or misstatement. When assessing materiality, entities should consider the characteristics of the users of its financial statements. It can be assumed that these users have a knowledge of business and accounting. To aid user understanding, financial statements should show material classes of items separately. Immaterial items may be aggregated with amounts of a similar nature, as long as this does not reduce understandability.
Offsetting IAS 1 says that assets and liabilities, and income and expenses, should only be offset when required or permitted by an IFRS standard. Comparative information Comparative information for the previous period should be disclosed.
Disclosures
Disclosure note presentation IAS 1 says that entities must present their disclosure notes in a systematic order. This might mean:
- Giving prominence to the most relevant areas • Grouping items measured in similar ways, such as assets held at fair value • Following the order in which items are presented in the statement of profit or loss and the statement of financial position.
Compliance with IFRS Standards Entities should make an explicit and unreserved statement that their financial statements comply with IFRS Standards.
Accounting policies Entities must produce an accounting policies disclosure note that details:
- the measurement basis (or bases) used in preparing the financial statements (e.g. historical cost, fair value, etc) • each significant accounting policy.
Sources of uncertainty An entity should disclose information about the key sources of estimation uncertainty that may cause a material adjustment to assets and liabilities within the next year, e.g. key assumptions about the future.
Reclassification adjustments Reclassification adjustments are amounts ‘recycled’ from other comprehensive income to profit or loss. IAS 1 requires that reclassification adjustments are disclosed, either on the face of the statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income or in the notes.
Dividends Distributions to equity holders are disclosed in the statement of changes. This requirement is in line with separate disclosure of owner and non-owner changes in equity discussed earlier.
This was the IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements and thanks for reading this. I hope you like this article.







The information has been useful to me. Thanks so much